Thrombocytosis: What Causes High Platelet Counts?
Thrombocytosis is a condition marked by a high platelet count in the blood. Platelets, the tiny cell fragments responsible for clotting, play a crucial role in maintaining our health. However, when their numbers soar beyond the normal range, it could signal an underlying health issue. Understanding the causes behind this condition is pivotal for effective management and treatment. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the various factors contributing to thrombocytosis. We will also shed light on its symptoms, diagnosis, and potential treatments.
What is Thrombocytosis?
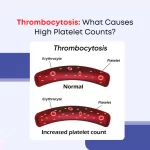
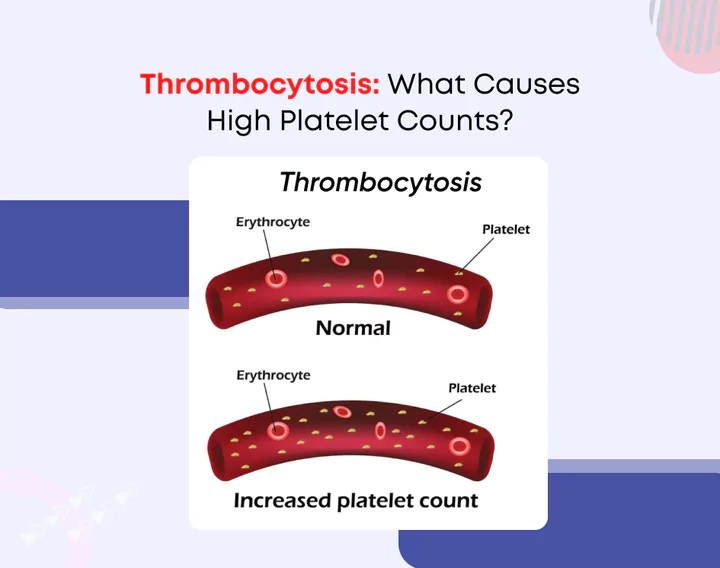
Thrombocytosis, also known as high platelet count, occurs when there is an excess of platelets in the blood circulation. These platelets are crucial for clotting. However, an abnormal increase in their numbers can lead to various health complications.
Platelet Count Range: Normal vs. Elevated
Platelet count in a healthy adult typically ranges between 150,000 and 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. Thrombocytosis is diagnosed when this count exceeds 450,000 platelets per microliter.
Primary vs. Secondary Thrombocytosis
Thrombocytosis can be classified into two main types: primary and secondary. Primary thrombocytosis, also called essential thrombocythemia, develops because of bone marrow abnormalities. Secondary thrombocytosis, on the other hand, is triggered by external factors or underlying medical conditions.
Importance of Platelets in the Body
Platelets play a crucial role in blood clotting (hemostasis), which is essential for stopping bleeding when we’re injured. They adhere to the site of injury and aggregate to form a plug, preventing excessive blood loss.
Knowing the basics of thrombocytosis sets the stage for exploring its causes and implications.
Essential Thrombocythemia
Primary thrombocytosis, also termed essential thrombocythemia, stems from abnormalities in the bone marrow, where platelets are produced. This condition is characterized by platelet overproduction, leading to elevated levels in the bloodstream.
- Genetic Factors and Inherited Mutations
Genetic mutations, such as mutations in the JAK2 gene, are commonly associated with primary thrombocytosis. These mutations can lead to the uncontrolled proliferation of platelet-producing cells in the bone marrow.
- JAK2 Mutation: A Common Culprit
The JAK2 mutation is one of the most prevalent genetic abnormalities found in individuals with primary thrombocytosis. This mutation results in the dysregulation of signalling pathways involved in platelet production, leading to excessive platelet formation.
- Bone Marrow Disorders and Their Role
Certain bone marrow disorders, such as myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs), can cause primary thrombocytosis. In these disorders, the bone marrow produces too many of certain types of blood cells, including platelets.
Primary thrombocytosis highlights the intricate interplay between genetic predispositions and bone marrow dysfunction.
Secondary Thrombocytosis
Unlike primary thrombocytosis, secondary thrombocytosis is triggered by external factors or underlying medical conditions. These conditions stimulate the body to produce more platelets as a response to specific stressors or diseases.
- Inflammatory Conditions and Infections
Inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease, can induce secondary thrombocytosis. Similarly, bacterial or viral infections can also trigger an increase in platelet production.
- Surgical Procedures and Trauma
Surgical procedures, trauma, or significant blood loss can lead to secondary thrombocytosis. How? The body attempts to replenish its platelet reserves to aid in wound healing and recovery.
- Chronic Diseases: Diabetes, Cancer, and more
Chronic diseases like diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and certain types of cancer can cause secondary thrombocytosis. These conditions disrupt normal physiological processes, leading to an overproduction of platelets.
Secondary thrombocytosis underscores the diverse array of factors that can influence platelet production in the body.
Symptoms and Diagnostic Approaches
Thrombocytosis often manifests with subtle or nonspecific symptoms, making diagnosis challenging without proper evaluation. Learning about these symptoms is crucial for timely intervention and management.
- Fatigue and Weakness
Excessive fatigue and weakness are common symptoms of thrombocytosis. They often attribute to the increased demand for the body’s clotting mechanisms.
- Headaches and Dizziness
Headaches and dizziness may occur due to disturbances in blood flow caused by the formation of blood clots. This is a potential complication of thrombocytosis.
- Risk of Blood Clots
Thrombocytosis increases the risk of blood clots (thrombosis). This can result in serious complications such as stroke, heart attack, or pulmonary embolism.
- Diagnostic Approaches:
Accurate diagnosis of thrombocytosis involves a combination of medical history review and physical examination. Laboratory tests such as complete blood count (CBC) and bone marrow biopsy are also essential.
Recognizing the symptoms and employing appropriate diagnostic methods are vital steps in addressing thrombocytosis effectively.
Thrombocytosis: Treatment Options and Management Strategies
Treatment for thrombocytosis aims to reduce platelet counts and mitigate associated risks such as blood clot formation. The approach to treatment depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition.
- Therapeutic Phlebotomy
Therapeutic phlebotomy is a procedure recommended for individuals with significantly elevated platelet counts. It involves drawing blood to reduce the number of circulating platelets.
- Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help manage thrombocytosis and reduce the risk of complications. This includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, and quitting smoking.
- Management Strategies:
A holistic approach to management involves several key steps in addition to medical interventions. These include regularly monitoring platelet counts, managing underlying medical conditions, and addressing risk factors for thrombosis.
Winding Up
Exploring treatment options and adopting holistic management strategies empower individuals in combating thrombocytosis and enhancing overall well-being.
Thrombocytosis poses significant health implications, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of its causes, symptoms, and management strategies. This condition underscores the intricate balance within the body’s hematopoietic system, whether primary or secondary.
We can strive towards optimal health and well-being by delving into its nuances and exploring effective treatment modalities. Let’s continue to stay informed, vigilant, and proactive in our journey towards combating thrombocytosis and promoting a healthier tomorrow.